Automate Document Signing using the DocuSign API
Adam Yue
Nov. 16, 2021
/
kube-bench is a Go application that can verify if an Openshift cluster is deployed securely by running the checks documented in the CIS Kubernetes Benchmark.
Please note that this tool only checks the CIS automation parts, for the manual portion, you will still need to follow the guideline to check the security settings manually, you can download the full CIS check guideline here.
You can refer to the official installation document to install kube-bench in your server.
For example:
$ curl -L https://github.com/aquasecurity/kube-bench/releases/download/v0.3.1/kube-bench_0.3.1_linux_amd64.rpm -o kube-bench_0.3.1_linux_amd64.rpm
$ sudo yum install kube-bench_0.3.1_linux_amd64.rpm -y
Unfortunately, kube-bench is not supported on OpenShift 4.x. For OpenShift 4.x, you would probably need to refer to the CIS policy for K8s and verify them one by one manually.
Following is the example of running kube-bench on our OpenShift 3.11 platform.
On compute nodes:
$ /usr/local/bin/kube-bench node --version ocp-3.11
[INFO] 2 Worker Node Security Configuration
[INFO] 7 Kubelet
[INFO] 7.1 Use Security Context Constraints to manage privileged containers as needed
[INFO] 7.2 Ensure anonymous-auth is not disabled
[PASS] 7.3 Verify that the --authorization-mode argument is set to WebHook
[PASS] 7.4 Verify the OpenShift default for the client-ca-file argument
[PASS] 7.5 Verify the OpenShift default setting for the read-only-port argument
[PASS] 7.6 Adjust the streaming-connection-idle-timeout argument
[INFO] 7.7 Verify the OpenShift defaults for the protect-kernel-defaults argument
[PASS] 7.8 Verify the OpenShift default value of true for the make-iptables-util-chains argument
[FAIL] 7.9 Verify that the --keep-terminated-pod-volumes argument is set to false
[INFO] 7.10 Verify the OpenShift defaults for the hostname-override argument
[PASS] 7.11 Set the --event-qps argument to 0
[PASS] 7.12 Verify the OpenShift cert-dir flag for HTTPS traffic
[PASS] 7.13 Verify the OpenShift default of 0 for the cadvisor-port argument
[PASS] 7.14 Verify that the RotateKubeletClientCertificate argument is set to true
[PASS] 7.15 Verify that the RotateKubeletServerCertificate argument is set to true
[INFO] 8 Configuration Files
[PASS] 8.1 Verify the OpenShift default permissions for the kubelet.conf file
[PASS] 8.2 Verify the kubeconfig file ownership of root:root
[FAIL] 8.3 Verify the kubelet service file permissions of 644
[WARN] 8.4 Verify the kubelet service file ownership of root:root
[PASS] 8.5 Verify the OpenShift default permissions for the proxy kubeconfig file
[PASS] 8.6 Verify the proxy kubeconfig file ownership of root:root
[PASS] 8.7 Verify the OpenShift default permissions for the certificate authorities file.
[PASS] 8.8 Verify the client certificate authorities file ownership of root:root
On master nodes:
$ /usr/local/bin/kube-bench master --version ocp-3.11
[INFO] 1 Securing the OpenShift Master
[INFO] 1 Protecting the API Server
[INFO] 1.1 Maintain default behavior for anonymous access
[PASS] 1.2 Verify that the basic-auth-file method is not enabled
[INFO] 1.3 Insecure Tokens
[PASS] 1.4 Secure communications between the API server and master nodes
[PASS] 1.5 Prevent insecure bindings
[PASS] 1.6 Prevent insecure port access
[PASS] 1.7 Use Secure Ports for API Server Traffic
[INFO] 1.8 Do not expose API server profiling data
[PASS] 1.9 Verify repair-malformed-updates argument for API compatibility
[PASS] 1.10 Verify that the AlwaysAdmit admission controller is disabled
[FAIL] 1.11 Manage the AlwaysPullImages admission controller
[INFO] 1.12 Use Security Context Constraints instead of DenyEscalatingExec admission
[INFO] 1.13 Use Security Context Constraints instead of the SecurityContextDeny admission controller
[PASS] 1.14 Manage the NamespaceLifecycle admission controller
[PASS] 1.15 Configure API server auditing - audit log file path
[FAIL] 1.16 Configure API server auditing - audit log retention
[FAIL] 1.17 Configure API server auditing - audit log backup retention
[FAIL] 1.18 Configure audit log file size
[PASS] 1.19 Verify that authorization-mode is not set to AlwaysAllow
[PASS] 1.20 Verify that the token-auth-file flag is not set
[PASS] 1.21 Verify the API server certificate authority
[PASS] 1.22 Verify the API server client certificate and client key
[INFO] 1.23 Verify that the service account lookup flag is not set
[INFO] 1.24 Verify the PodSecurityPolicy is disabled to ensure use of SecurityContextConstraints
[PASS] 1.25 Verify that the service account key file argument is not set
[PASS] 1.26 Verify the certificate and key used for communication with etcd
[FAIL] 1.27 Verify that the ServiceAccount admission controller is enabled
[PASS] 1.28 Verify the certificate and key used to encrypt API server traffic
[PASS] 1.29 Verify that the --client-ca-file argument is not set
[PASS] 1.30 Verify the CA used for communication with etcd
[INFO] 1.31 Verify that the authorization-mode argument is not set
[PASS] 1.32 Verify that the NodeRestriction admission controller is enabled
[FAIL] 1.33 Configure encryption of data at rest in etcd datastore
[FAIL] 1.34 Set the encryption provider to aescbc for etcd data at rest
[FAIL] 1.35 Enable the EventRateLimit plugin
[PASS] 1.36 Configure advanced auditing
[WARN] 1.37 Adjust the request timeout argument for your cluster resources
[INFO] 2 Scheduler
[INFO] 2.1 Verify that Scheduler profiling is not exposed to the web
[INFO] 3 Controller Manager
[FAIL] 3.1 Adjust the terminated-pod-gc-threshold argument as needed
[INFO] 3.2 Verify that Controller profiling is not exposed to the web
[PASS] 3.3 Verify that the --use-service-account-credentials argument is set to true
[FAIL] 3.4 Verify that the --service-account-private-key-file argument is set as appropriate
[FAIL] 3.5 Verify that the --root-ca-file argument is set as appropriate
[INFO] 3.6 Verify that Security Context Constraints are applied to Your Pods and Containers
[FAIL] 3.7 Manage certificate rotation
[INFO] 4 Configuration Files
[PASS] 4.1 Verify the OpenShift default permissions for the API server pod specification file
[PASS] 4.2 Verify the OpenShift default file ownership for the API server pod specification file
[PASS] 4.3 Verify the OpenShift default file permissions for the controller manager pod specification file
[PASS] 4.4 Verify the OpenShift default ownership for the controller manager pod specification file
[PASS] 4.5 Verify the OpenShift default permissions for the scheduler pod specification file
[FAIL] 4.6 Verify the scheduler pod specification file ownership set by OpenShift
[PASS] 4.7 Verify the OpenShift default etcd pod specification file permissions
[PASS] 4.8 Verify the OpenShift default etcd pod specification file ownership
[FAIL] 4.9 Verify the default OpenShift Container Network Interface file permissions
[PASS] 4.10 Verify the default OpenShift Container Network Interface file ownership
[PASS] 4.11 Verify the default OpenShift etcd data directory permissions
[PASS] 4.12 Verify the default OpenShift etcd data directory ownership
[PASS] 4.13 Verify the default OpenShift admin.conf file permissions
[PASS] 4.14 Verify the default OpenShift admin.conf file ownership
[PASS] 4.15 Verify the default OpenShift scheduler.conf file permissions
[PASS] 4.16 Verify the default OpenShift scheduler.conf file ownership
[PASS] 4.17 Verify the default Openshift controller-manager.conf file permissions
[PASS] 4.18 Ensure that the controller-manager.conf file ownership is set to root:root (Scored)
[INFO] 5 Etcd
[PASS] 5.1 Verify the default OpenShift cert-file and key-file configuration
[FAIL] 5.2 Verify the default OpenShift setting for the client-cert-auth argument
[PASS] 5.3 Verify the OpenShift default values for etcd_auto_tls
[FAIL] 5.4 Verify the OpenShift default peer-cert-file and peer-key-file arguments for etcd
[PASS] 5.5 Verify the OpenShift default configuration for the peer-client-cert-auth
[FAIL] 5.6 Verify the OpenShift default configuration for the peer-auto-tls argument
[INFO] 5.7 Optionally modify the wal-dir argument
[INFO] 5.8 Optionally modify the max-wals argument
[PASS] 5.9 Verify the OpenShift default configuration for the etcd Certificate Authority
[INFO] 6 General Security Primitives
[WARN] 6.1 Ensure that the cluster-admin role is only used where required
[WARN] 6.2 Verify Security Context Constraints as in use
[WARN] 6.3 Use OpenShift projects to maintain boundaries between resources
[WARN] 6.4 Create network segmentation using the Multi-tenant plugin or Network Policies
[WARN] 6.5 Enable seccomp and configure custom Security Context Constraints
[WARN] 6.6 Review Security Context Constraints
[WARN] 6.7 Manage Image Provenance using ImagePolicyWebhook admission controller
[WARN] 6.8 Configure Network policies as appropriate
[WARN] 6.9 Use Security Context Constraints as compensating controls for privileged containers
...
Falco is used for Kubernetes runtime security. Installing Falco directly on the host system is considered the most secure approach so that Falco is isolated from Kubernetes and the Falco alerts can be consumed via read-only agents running in Kubernetes.
You can set up the Falco Operator via OperatorHub
https://catalog.redhat.com/software/operators/detail/5f746115c646d579f6489fb5
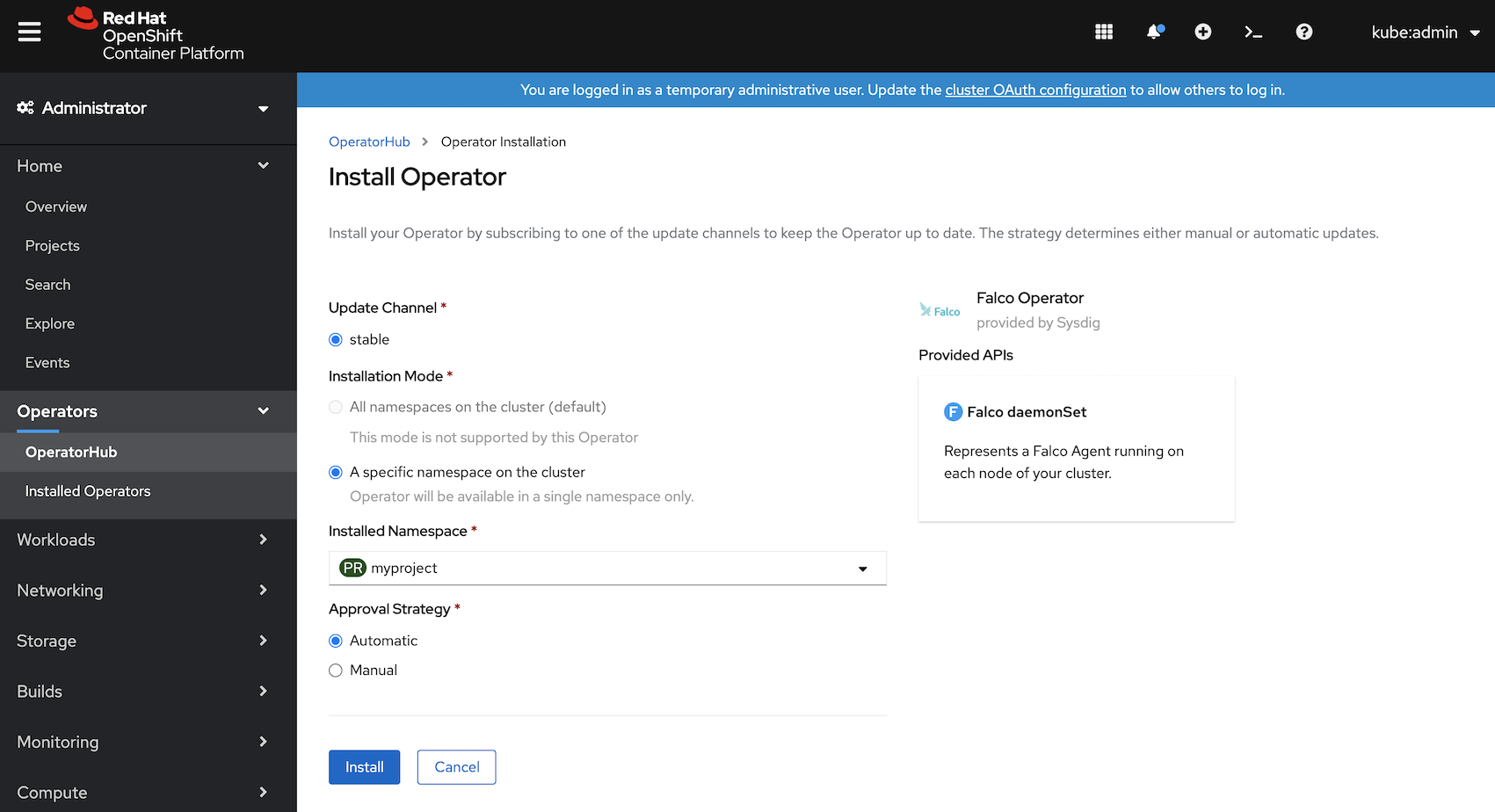
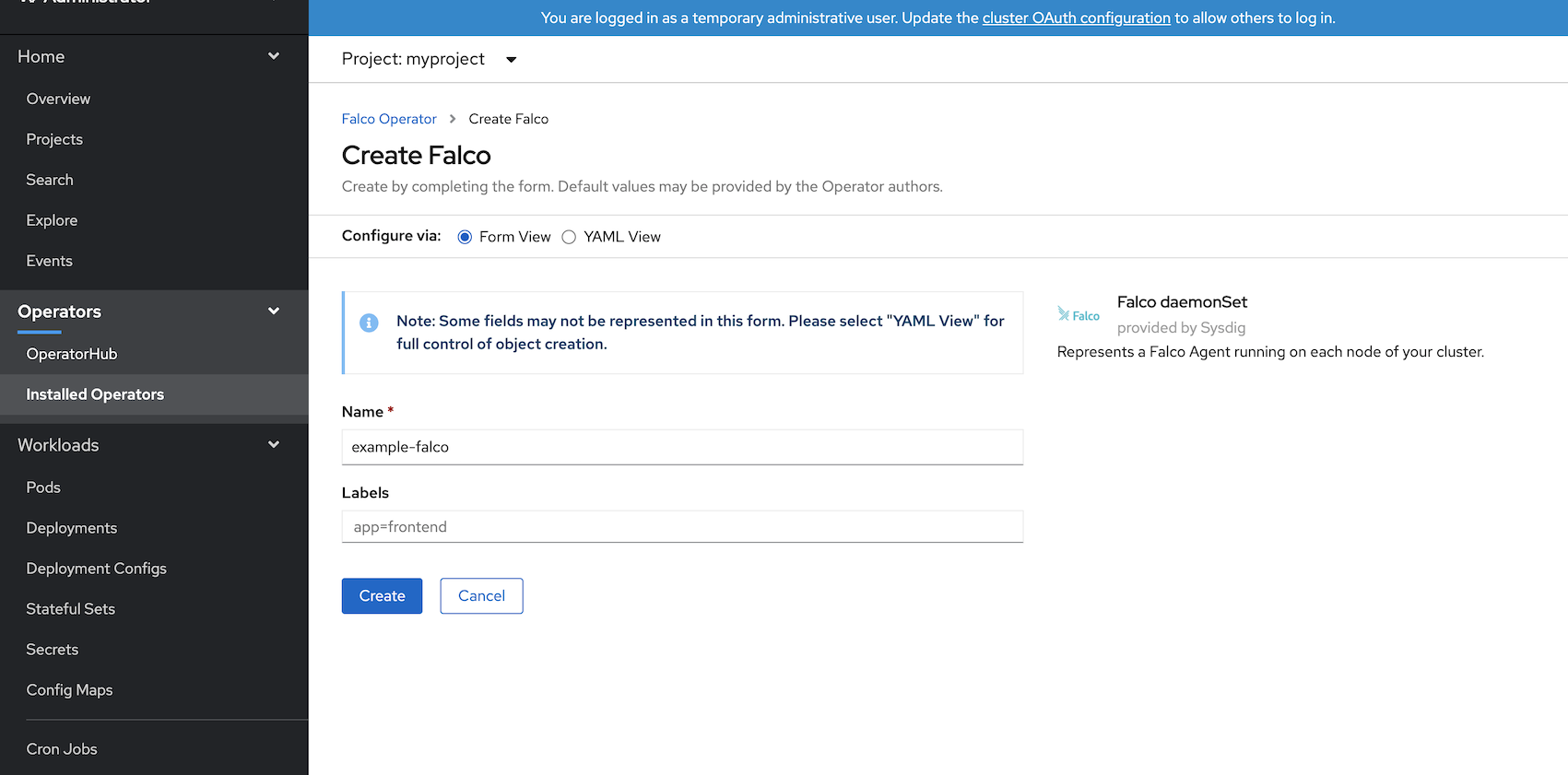
For example, we want to show alert logs when someone runs a bash shell inside the container
Add the following rule to the YAML of Falco DaemonSet
- macro: shell_procs
condition: proc.name in (shell_binaries)
output: shell in a container (user=%user.name container_id=%container.id container_name=%container.name shell=%proc.name parent=%proc.pname cmdline=%proc.cmdline)
priority: WARNING
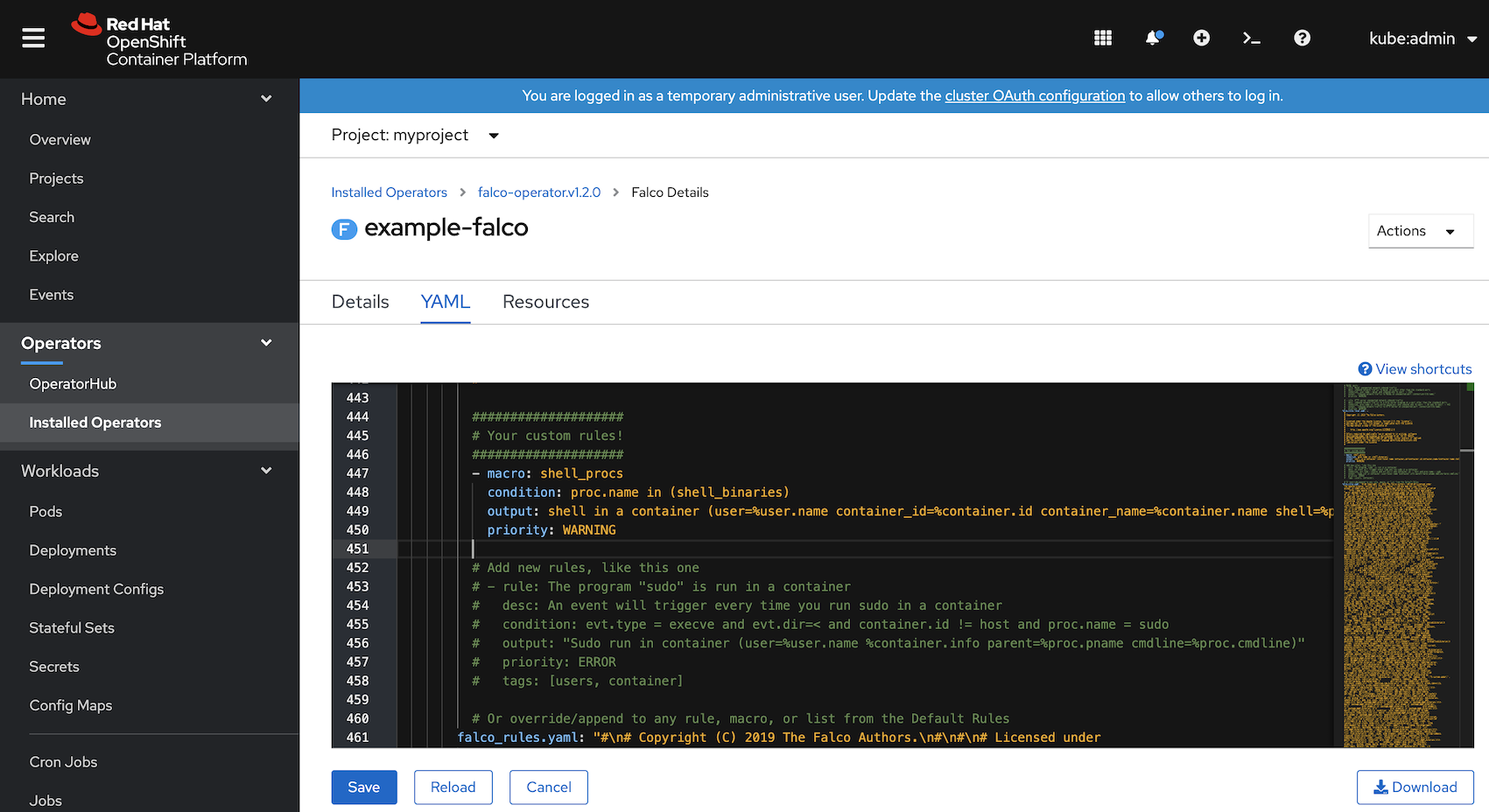
When someone tries to run "oc rsh" into a pod, you can find the warning logs for the custom alert in the daemonset pods.
$ oc logs -f ds/example-falco
...
04:54:40.373142233: Notice A shell was spawned in a container with an attached terminal (user=<NA> k8s.ns=myproject k8s.pod=nginx-pod container=d165df35e317 shell=sh parent=runc cmdline=sh -c TERM="xterm-256color" /bin/sh terminal=34817 container_id=d165df35e317 image=<NA>) k8s.ns=myproject k8s.pod=nginx-pod container=d165df35e317
04:54:40.375631721: Notice A shell was spawned in a container with an attached terminal (user=<NA> k8s.ns=myproject k8s.pod=nginx-pod container=d165df35e317 shell=sh parent=runc cmdline=sh terminal=34817 container_id=d165df35e317 image=<NA>) k8s.ns=myproject k8s.pod=nginx-pod container=d165df35e317
To protect your applications and platform as a whole, you should consider to:
Address
Level 8
11-17 York Street
Sydney NSW 2000
Phone Number
+61 2 8294 8067
Email
[email protected]

By Adam Yue
By Felix Schmitz
© 2017-2024 Darumatic Pty Ltd. All Rights Reserved.